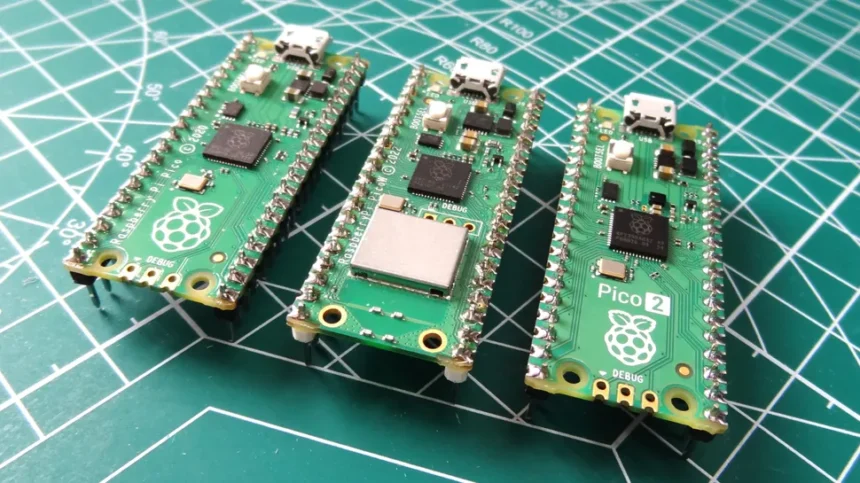
The Raspberry Pi Pico 2 is an evolution of the original Raspberry Pi Pico, which made waves in the microcontroller community with its impressive balance of performance, power efficiency, and affordability. This document will provide an overview of the Raspberry Pi Pico 2, followed by a review comparing it to its predecessor, the Raspberry Pi Pico, highlighting the key differences and improvements.
1. Overview of Raspberry Pi Pico 2
The Raspberry Pi Pico 2 retains the core philosophy of being a low-cost microcontroller, built around the RP2040 chip, but it introduces several enhancements that make it even more versatile for a broader range of projects.
- Processor: Like the original Pico, the Pico 2 is powered by the RP2040 microcontroller, a dual-core Arm Cortex-M0+ processor running at 133 MHz.
- Memory: It still features 264KB of SRAM, but with more efficient memory management.
- Storage: The flash storage remains at 2MB, but the Pico 2 supports expanded storage options through an external flash memory interface.
- Connectivity: A significant upgrade is the inclusion of Wi-Fi support, making it ideal for IoT projects right out of the box without needing an external Wi-Fi module.
- Power Supply: Power delivery and management have been optimized, offering better battery life in portable applications.
- GPIO: The GPIO pins remain the same, with 26 multifunctional GPIO pins, including three ADCs, but there is enhanced support for advanced interfacing protocols like CAN and I2C.
- Form Factor: The form factor and pinout remain identical to ensure compatibility with existing Raspberry Pi Pico projects and accessories.
2. Comparison: Raspberry Pi Pico 2 vs. Raspberry Pi Pico
Image Credit : Future
| Feature | Raspberry Pico | Raspberry Pico 2 |
| Processor | RP2040, Dual-core Arm Cortex-M0+ | RP2040, Dual-core Arm Cortex-M0+ |
| Clock Speed | 133 MHz | 133 MHz |
| Memory (SRAM) | 264 KB | 264 KB |
| Flash Storage | 2 MB | 2 MB (expandable) |
| Connectivity | None | Wi-Fi |
| GPIO Pins | 26 (3 ADCs) | 26 (3 ADCs) |
| Power Supply | 1.8–5.5V | 1.8–5.5V (optimized) |
| Form Factor | 51mm x 21mm, identical pinout | 51mm x 21mm, identical pinout |
| Price | ~$4 | ~$6-8 |
3. Main Differences
- Wi-Fi Connectivity: The most notable difference between the Raspberry Pi Pico 2 and the original Raspberry Pi Pico is the inclusion of built-in Wi-Fi on the Pico 2. This addition transforms the Pico 2 into a fully-fledged IoT-ready device without needing any external modules.
- Storage Expansion: While both models feature 2MB of flash storage, the Pico 2 introduces the capability for external storage expansion, which is particularly beneficial for projects that require more storage space.
- Power Management: The Pico 2 features improved power management, making it more efficient, especially for battery-powered applications. This improvement is subtle but important for portable projects.
- Advanced Interface Support: The Pico 2 has better support for advanced interfacing protocols like CAN, which can be essential for more complex communication tasks in embedded systems.
- Price: With the additional features, the Pico 2 is slightly more expensive than the original Pico, but the price difference is justified by the enhancements, especially the integrated Wi-Fi.
4. Review and Conclusion
The Raspberry Pi Pico 2 is a significant step up from the original Pico, especially for those looking to incorporate wireless connectivity into their projects. The built-in Wi-Fi alone makes it a compelling choice for IoT developers, educators, and hobbyists who previously relied on external modules to achieve similar functionality.
Pros:
- Integrated Wi-Fi makes it ideal for IoT applications.
- Storage expansion adds flexibility.
- Improved power management for better battery life.
- Maintains the same form factor and GPIO pinout, ensuring compatibility with existing projects.
Cons:
- Slightly more expensive than the original Pico.
- The enhancements might not justify the upgrade for projects that don’t require Wi-Fi or additional storage.
The Raspberry Pi Pico 2 is an excellent choice for anyone starting new projects that require connectivity or need more robust interfacing options. For those with existing Pico-based projects, upgrading to the Pico 2 might not be necessary unless the additional features are required.
Overall, the Pico 2 solidifies its place as a versatile, powerful, and cost-effective microcontroller, continuing the legacy of the Raspberry Pi ecosystem while offering key enhancements that open up new possibilities.