Crypto++ is a free and open-source C++ class library for cryptographic algorithms made by Wei Dai. It provides a comprehensive suite of tools for secure communication and data protection. This article delves into the core functionalities, usage, and advanced topics of the Crypto++ library.
Understanding Crypto++
Crypto++ offers a wide range of cryptographic primitives, including:
- Block ciphers: AES, DES, Triple DES, Blowfish, Camellia, CAST-128, and more.
- Stream ciphers: ARC4, Salsa20, ChaCha20, and others.
- Hash functions: MD5, SHA-1, SHA-2, RIPEMD, and more.
- Message authentication codes (MACs): HMAC, CMAC, Poly1305, and others.
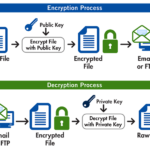
- Public-key cryptography: RSA, DSA, Elliptic Curve Cryptography (ECC), and Diffie-Hellman.
- Random number generators (RNGs): Various high-quality RNGs.
Basic Usage
To use Crypto++, include the necessary header files in your C++ code:
#include <cryptopp/cryptlib.h>
#include <cryptopp/aes.h> // For AES example
Create instances of cryptographic objects and use their member functions to perform cryptographic operations.
#include <iostream>
#include <cryptopp/cryptlib.h>
#include <cryptopp/aes.h>
int main()
{
CryptoPP::AutoSeededRandomPool rng;
CryptoPP::AES::Encryption aesEncryption(CryptoPP::AES::DEFAULT_KEYLENGTH);
aesEncryption.SetKeyWithIV(key, CryptoPP::AES::DEFAULT_KEYLENGTH, iv);
// ... encryption and decryption logic ...
return 0;
}
Key Concepts and Best Practices
- Randomness: Crypto++ offers various RNGs. Always use a cryptographically secure random number generator (CSPRNG) for key generation and initialization vectors.
- Key Management: Proper key generation, storage, and distribution are crucial. Use strong key derivation functions (KDFs) to generate keys from passwords.
- Padding: Most block ciphers require padding to handle data lengths that are not multiples of the block size. Crypto++ provides padding schemes like PKCS#7.
- Modes of Operation: Different modes of operation (ECB, CBC, CTR, GCM, etc.) offer varying levels of security and performance. Choose the appropriate mode based on your requirements.
- Error Handling: Crypto++ provides mechanisms for error handling. Check return values and exceptions to ensure correct operation.
- Performance: Consider performance implications when choosing algorithms and implementations. Crypto++ offers optimized implementations for many algorithms.
Advanced Topics
Cryptographic Protocols
Crypto++ can be used to implement various cryptographic protocols, such as:
- TLS/SSL: Secure communication protocols.
- SSH: Secure shell protocol.
- IPsec: Secure network communication.
Digital Signatures
Crypto++ supports digital signature algorithms like RSA and DSA. These can be used for authentication, integrity, and non-repudiation.
Key Derivation Functions (KDFs)
KDFs are essential for generating cryptographic keys from passwords or other secrets. Crypto++ provides KDFs like PBKDF2 and bcrypt.
Cryptographic Hash Functions
Hash functions are used for data integrity, message authentication, and digital signatures. Crypto++ offers a variety of hash functions with different security levels.
Elliptic Curve Cryptography (ECC)
ECC is a public-key cryptography system that offers smaller key sizes compared to RSA for equivalent security levels. Crypto++ supports ECC for various curve parameters.
Cryptographic Modes of Operation
Crypto++ provides implementations of different block cipher modes of operation, including ECB, CBC, CTR, GCM, and others. Understanding the strengths and weaknesses of each mode is crucial for selecting the appropriate one.
Security Considerations
- Algorithm Selection: Choose algorithms that are considered secure and have undergone thorough cryptanalysis.
- Key Length: Use appropriate key lengths to ensure adequate security.
- Implementation Correctness: Implement cryptographic algorithms correctly to avoid vulnerabilities.
- Randomness: Use high-quality random number generators.
- Side-Channel Attacks: Be aware of potential side-channel attacks and take countermeasures if necessary.